- The IPRC Statement of Decision
- Flowchart for the Appeals Process after the IPRC meeting
- The second IPRC meeting
- Flowchart on the Important deadlines for IPRC Appeals
- Filing a Notice of Appeal with the SEAB
- The SEAB panel members
- What if I have questions before the SEAB hearing
- When is the hearing held and what can I do to prepare?
- Can I bring a support person to the SEAB hearing?
- The SEAB hearing
- The Special Education Tribunal (SET)
- The SET process
The IPRC Statement of Decision
As soon as possible after a decision is made, the Identification, Placement, and Review Committee (IPRC) must provide a written statement of their decision to the parent/caregiver and student 16+. This is called the Statement of Decision.
If the committee identifies the student as exceptional, the decision must include:
- The category and definition of exceptionality
- Strengths and needs of the student
- Placement decision
- Reasons for placement in special education class, if that is the decision
- Recommendations for a special education program and/or services
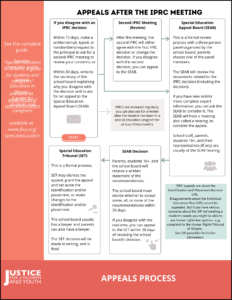
Once you receive the IPRC Statement of Decision, you can:
Agree with the decision, or
Disagree with the decision and:
- Choose not to appeal. The student will be placed after 30 days
- Request a second IPRC meeting to review your concerns, within 15 days,
- File an appeal with the Special Education Appeal Board (SEAB), within 30 days
Flowchart for the Appeals Process after the IPRC meeting
The second IPRC meeting
The IPRC is intended to support the student, but there are times when a parent and/or student 16+ may not agree with the IPRC decision. The disagreement may be about the placement and/or the identification.
To schedule a second IPRC meeting:
- Make a written request to the principal asking to talk about your concerns. This request must be made within 15 days of receiving the IPRC written statement of decision.
- Include what you disagree with, and the reasons why you disagree. Include any new information or documentation you have received from experts.
The IPRC team will then meet again to review their first decision. They will also read and consider any new information you provided to support your case in requesting a review. The IPRC must send their second decision in writing to the parent and student 16+ as soon as possible.
If you still disagree with the second decision, you can choose to file a Notice of Appeal with the Special Education Appeal Board (SEAB). This must be done within 15 days of receiving the second/review decision.
You can choose to skip the second meeting step and go straight to an Appeal.
Flowchart on the Important deadlines for IPRC Appeals:
Filing a Notice of Appeal with the SEAB
To appeal the decision of the IPRC to the Special Education Appeal Board (SEAB), you must file a Notice of Appeal with the secretary of the school board. You must file the appeal within 30 days of the original IPRC written decision or within 15 days of the second IPRC review decision. The secretary of the board is usually the Director of Education for your school board. You can find out who this is by asking the principal of your school, or searching online.
The Notice of Appeal must include:
- WHAT you disagree with (identification and/or placement), and
- WHY you disagree with the decision
If you have further information and/or documents from experts that can be shared, such as medical reports or a new psychoeducational assessment, say so clearly in your notice of appeal letter.
Keeping to timelines is very important. As long as it is submitted on time, the request for an appeal should be accepted even if the notice is incorrectly written, or does not accurately describe the area of disagreement.
When a notice of appeal has been filed, the IPRC placement is put on hold. Parents & student 16+ can work with the school board to put in a temporary placement, pending the final results of the appeal.
The SEAB panel members
The Special Education Appeal Board (SEAB) will be made up of a panel of three people who will hear your appeal about the
identification and/or placement of the student.
The three SEAB members are:
- Representative selected by the school board
- Representative selected by the parent. Example: someone from a community organization. If you are not aware of any, the school board can provide a list. You cannot select a Ministry of Education employee or a member of the school board.
- A chairperson, selected by the first two representatives
The SEAB is a more formal process than an IPRC meeting. Their decision gives recommendations to the school board. The recommendations are persuasive, but the school board has the choice to accept or reject the recommendations.
What if I have questions before the SEAB hearing
The school board must appoint a member of their staff to be the contact person, who will organize and prepare for the meeting. Their role includes:
- letting you know how they will be sharing information (e.g. via email, or phone)
- being the contact person for any questions
- finding the meeting space – it must be a neutral space and reasonably close to the parents’ home
- ensuring that parents and student 16+
- are aware of their right to have a representative at the meeting
When is the hearing held and what can I do to prepare?
The meeting must be held at a convenient time and place, but no later than 30 days after the Chair of the SEAB has been selected. The meeting can be held at a later date if the parent/student 16+ and school board have all agreed in writing.
If you have new or updated information, you should submit your documents to the board contact person and inform them that you would like it considered at the meeting.
Can I bring a support person to the SEAB hearing?
In addition to submitting any new or helpful documentation, parents and students 16+ are entitled to be present for, and participate, in all discussions.
Parents and students 16+ are also entitled to have a representative at the hearing as a support, or to speak on their behalf.
The support person is different than the panel member that is chosen by the parent/student 16+. You can bring anyone that you feel will help you through the process. It could be a trusted adult, a family friend, or an advocate or staff member from a community organization.
Before the hearing, talk through your concerns about the IPRC decision(s) with the person you’ve invited to be your support. You want to be clear on what you want from the hearing, as well as be clear with the support person what you want their role to be at the hearing.
The SEAB hearing
The school board or SEAB must give you written notice of at least 10 days before the appeal board meets.
During the hearing, the SEAB panel members will review all prior IPRC decisions, any documents outlining the concerns with the decision(s) made, and will hear from any presenters.
After the hearing, the panel will provide a written statement of their recommendations and reasons for their recommendations.
Within 30 days of receiving the statement, the school board must decide whether to accept or reject the recommendations.
The school board must then send their notice of this decision to the parent and student 16+.
If you disagree with the school board’s decision to accept or reject the SEAB decision, you can file an appeal with the Special Education Tribunal (SET).
There is no legal requirement for an official file to be kept following the SEAB decision. Parents and students 16+ should keep copies of all information provided to them for their own records, including all written communications and notes about oral communications, any submitted information, the appeal board recommendations, and the school board decision.
The Special Education Tribunal (SET)
The Special Education Tribunal (SET) is the final place to appeal the identification and/or placement of a student.
If you do not agree with the school board’s decision to accept or reject the SEAB’s recommendations, you must write to the SET within 30 days of receiving the school board’s decision, to say that you would like to seek an appeal.
SET will send you a Form A: Notice of Appeal.
You have up to 20 days to complete and file the Form A. You should include the IPRC decision, SEAB recommendations, and school board’s decision to accept or reject the SEAB recommendations.
The school board has 10 days to file a response to your appeal with SET.
The SET has broad powers and the appeal is a formal hearing process. The school board usually has a lawyer, and parents may have a lawyer for the appeal.
If you are a caregiver or student needing help to find a lawyer for the appeal, contact us.
The SET process
As a first step, the SET will schedule a voluntary mediation prior to the prehearing conference, with the aim of settling the disagreement. If issues remain after mediation, a prehearing conference will be held and hearing dates will be set.
Hearings can take 1-5 days. Both sides will have a chance to present their arguments about what they think is the right identification and/or placement outcome for the student.
The decision from the SET will be made within 90 days of the hearing. The school and parent/student 16+ will receive the decision in writing.
There is no further process under the Education Act for appeals following the SET decision. The decision is final. Speak to a lawyer if you wish to consider further options to challenge the decision, outside the Education Act process.